Chapter 9C. Markings
Section 9C.01 Functions
of Markings
Support:
Markings indicate the separation of the lanes for road users, assist
the bicyclist by indicating assigned travel paths, indicate correct
position for traffic control signal actuation, and provide advance
information for turning and crossing maneuvers.
Section 9C.02 General Principles
Guidance:
Bikeway design guides should be used when designing markings for
bicycle facilities (see Section
9A.05).
Standard:
Markings used on bikeways shall be retroreflectorized.
Guidance:
Pavement marking symbols and/or word messages should be used in
bikeways where appropriate. Consideration should be given to selecting
pavement marking materials that will minimize loss of traction for
bicycles under wet conditions.
Standard:
The colors, width of lines, patterns of lines, and symbols used
for marking bicycle facilities shall be as defined in Sections 3A.04,
3A.05,
and 3B.22.
Support:
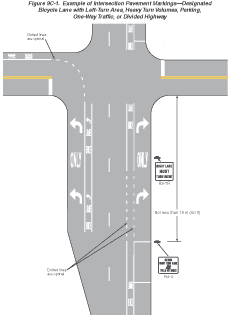
Figures 9B-7 and 9C-1 through 9C-8 show examples of the application
of lines, word messages, and symbols on designated bikeways.
Option:
A dotted line may be used to define a specific path for a bicyclist
crossing an intersection (see Figure 9C-1) as described in Sections
3A.05
and 3B.08.
Figure
9C-1 Example of Intersection Pavement Markings—Designated
Bicycle Lane with Left-Turn Area, Heavy Turn Volumes, Parking, One-Way
Traffic, or Divided Highway
Section 9C.03 Marking
Patterns and Colors on Shared-Use Paths
Option:
Where shared-use paths are of sufficient width to designate two
minimum width lanes, a solid yellow line may be used to separate
the two directions of travel where passing is not permitted, and
a broken yellow line may be used where passing is permitted (see
Figure 9C-2).
Figure
9C-2 Examples of Centerline Markings for Shared-Use Paths
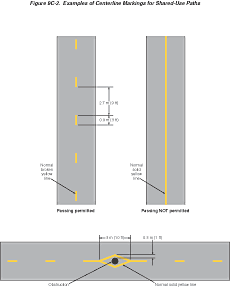
Guidance:
Broken lines used on shared-use paths should have the usual 1-to-3
segment-to-gap ratio. A nominal 0.9 m (3 ft) segment with a 2.7
m (9 ft) gap should be used.
If conditions make it desirable to separate two
directions of travel on shared-use paths at particular locations,
a solid yellow line should be used to indicate no passing and no
traveling to the left of the line.
Markings as shown in Figure 9C-2 should be used
at the location of obstructions in the center of the path, including
vertical elements intended to physically prevent unauthorized motor
vehicles from entering the path.
Option:
A solid white line may be used on shared-use paths to separate different
types of users. The R9-7 sign (see Figure 9B-2) may be used to supplement
the solid white line.
Smaller size letters and symbols may be used on
shared-use paths. Where arrows are needed on shared-use paths, half-size
layouts of the arrows may be used (see Section
3B.19).
Fixed objects adjacent to shared-use paths may be
marked with object markers (Type
1, 2, or 3).
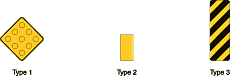
Standard:
All object markers shall be retroreflective.
Markers such as those described in Section
3C.01 shall also be used on shared-use paths, if needed.
Obstructions in the traveled way of a shared-use
path shall be marked with retroreflectorized material or appropriate
object markers.
On Type 3 markers, the alternating black and retroreflective
yellow stripes shall be sloped down at an angle of 45 degrees toward
the side on which traffic is to pass the obstruction.
Section 9C.04 Markings
For Bicycle Lanes
Guidance:
Longitudinal pavement markings should be used to define bicycle
lanes.
Support:
Pavement markings designate that portion of the roadway for preferential
use by bicyclists. Markings inform all road users of the restricted
nature of the bicycle lane.
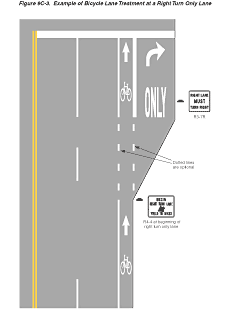
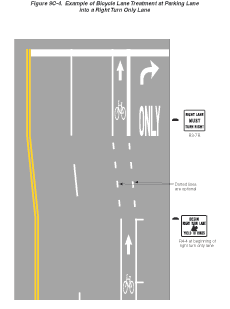
Examples of bicycle lane markings at right-turn
lanes are shown in Figures 9C-1,
9C-3, and 9C-4.
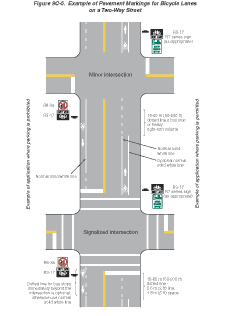
Examples of pavement markings for bicycle lanes on a two-way street
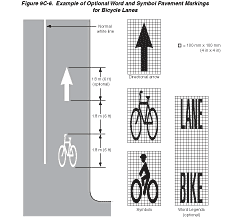
are shown in Figure 9C-5. Pavement symbols
and markings for bicycle lanes are shown in Figure
9C-6.
Standard:
If used, the bicycle lane symbol marking (see Figure 9C-6) shall
be placed immediately after an intersection and at other locations
as needed. The bicycle lane symbol marking shall be white. If the
bicycle lane symbol marking is used in conjunction with other word
or symbol messages, it shall precede them.
If the word or symbol pavement markings shown
in Figure 9C-6 are used, Bicycle Lane signs (see Section
9B.04) shall also be used, but the signs need not be adjacent
to every symbol to avoid overuse of the signs.
A through bicycle lane shall not be positioned
to the right of a right turn only lane.
Figure
9C-3 Example of Bicycle Lane Treatment at a Right Turn Only
Lane
Figure
9C-4 Example of Bicycle Lane Treatment at Parking Lane into
a Right Turn Only Lane
Figure
9C-5 Example of Pavement Markings for Bicycle Lanes on a Two-Way
Street
Figure
9C-6 Example of Optional Word and Symbol Pavement Markings for
Bicycle Lanes
Support:
A bicyclist continuing straight through an intersection from the
right of a right turn lane would be inconsistent with normal traffic
behavior and would violate the expectations of right-turning motorists.
Guidance:
When the right through lane is dropped to become a right turn only
lane, the bicycle lane markings should stop at least 100 feet before
the beginning of the right turn lane. Through bicycle lane markings
should resume to the left of the right turn only lane.
An optional through-right turn lane next to a
right turn only lane should not be used where there is a through
bicycle lane. If a capacity analysis indicates the need for an optional
through-right turn lane, the bicycle lane should be discontinued
at the intersection approach.
Posts or raised pavement markers should not be
used to separate bicycle lanes from adjacent travel lanes.
Support:
Using raised devices creates a collision potential for bicyclists
by placing fixed objects immediately adjacent to the travel path
of the bicyclist. In addition, raised devices can prevent vehicles
turning right from merging with the bicycle lane, which is the preferred
method for making the right turn. Raised devices used to define
a bicycle lane can also cause problems in cleaning and maintaining
the bicycle lane.
Standard:
Bicycle lanes shall not be provided on the circular roadway of a
roundabout intersection.
Section 9C.05 Bicycle
Detector Symbol
Option:
A symbol (see Figure 9C-7) may be placed on the pavement indicating
the optimum position for a bicyclist to actuate the signal.
Figure
9C-7 Example of Bicycle Detector Pavement Marking
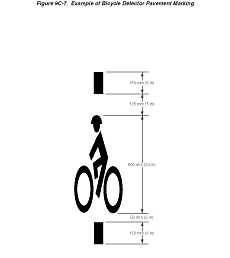
An R10-22 sign (see Section
9B.12 and Figure 9B-2) may
be installed to supplement the pavement marking.
Section 9C.06 Pavement
Markings for Obstructions
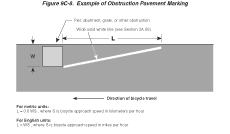
Guidance:
In roadway situations where it is not practical to eliminate a drain
grate or other roadway obstruction that is inappropriate for bicycle
travel, white markings applied as shown in Figure 9C-8 should be
used.
Figure
9C-8 Example of Obstruction Pavement Marking
Back to Top
|

