|
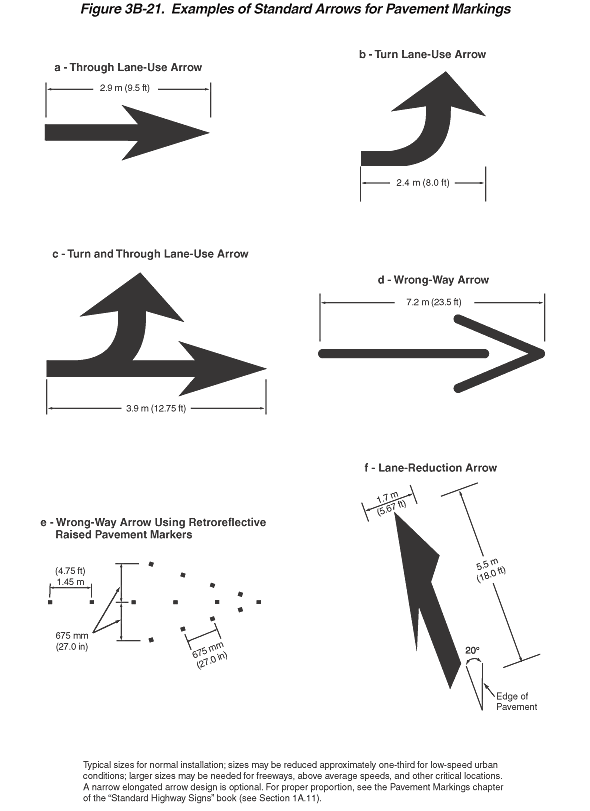
Figure 3B-21. Examples of Standard Arrows for Pavement Markings
This figure illustrates six examples of standard arrows for pavement
markings. In each example, black arrows are shown.
The figure shows examples (a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f):
- Example (a) shows a through lane-use arrow. It is composed of
a horizontal straight shaft that ends in an arrowhead, pointing
to the right. It is shown as 2.9 m (9.5 ft) long.
- Example (b) shows a turn lane-use arrow. It is composed of a
horizontal left-curving shaft that ends in an upward-pointing
arrowhead. It is shown as 2.4 m (8.0 ft) long.
- Example (c) shows a turn and through lane-use arrow. It is composed
of a horizontal shaft that branches. One branch becomes a left-curving
shaft that ends in an upward-pointing arrowhead, and the other
branch continues as a straight shaft that ends in an arrowhead,
pointing to the right. It is shown as 3.9 m (12.75 ft) long.
- Example (d) shows a wrong-way arrow. It is composed of a horizontal
straight shaft that is a thin rather than a thick line. A right-pointing
arrowhead is also composed of a thin rather than thick line. It
is at the right end of the shaft but is not connected to it. It
is shown as 7.2 m (23.5 ft) long.
- Example (e) shows a wrong-way arrow using retroreflective raised
pavement markers. A total of 14 retroreflective raised pavement
markers, each denoted in the example by a small black square,
are arranged in the shape of a right-pointing arrow. The markers
in the shaft are shown as 1.45 m (4.75 ft) apart, the markers
in the arrowhead are shown as 675 mm (27.0 in) apart, and the
width of each half of the arrowhead, above and below the shaft,
is shown as 675 mm (27.0 in).
- Example (f) shows a lane-reduction arrow. It is composed of
a straight shaft with a diagonally shaped base that ends in an
upward-pointing arrowhead. It is shown as 5.5 m (18.0 ft) long
and 1.7 m (5.67 ft) wide. The arrowhead is shown with a diagonally
shaped base, and the left side of the arrowhead is narrower than
the right. The arrow is shown in a vertical orientation but at
a 20-degree left angle from the right edge of the pavement.
A note states: "Typical sizes for normal installation; sizes
may be reduced approximately one-third for low-speed urban conditions;
larger sizes may be needed for freeways, above average speeds, and
other critical locations. A narrow elongated arrow design is optional.
For proper proportion, see the Pavement Markings chapter of the
'Standard Highway Signs' book (see Section
1A.11)."
Back
to Chapter 3B
|

